
Chinese Journal OF Rice Science ›› 2017, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 65-71.DOI: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6069
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Dong ZHAND, Lichao SHI, Jun YE*( ), Zhen’an HOU, Cunhu WANG, Yonghai WU
), Zhen’an HOU, Cunhu WANG, Yonghai WU
Received:2016-04-26
Revised:2016-07-12
Online:2017-01-20
Published:2017-01-10
Contact:
Jun YE
通讯作者:
冶军
基金资助:CLC Number:
Dong ZHAND, Lichao SHI, Jun YE, Zhen’an HOU, Cunhu WANG, Yonghai WU. Effects of Selenium Valence on Its Uptake and Translocation in Rice Under Drip Irrigation[J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2017, 31(1): 65-71.
张栋, 史力超, 冶军, 侯振安, 王存虎, 吴永海. 滴灌条件下不同价态外源硒对水稻硒吸收及转运的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2017, 31(1): 65-71.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.ricesci.cn/EN/10.16819/j.1001-7216.2017.6069
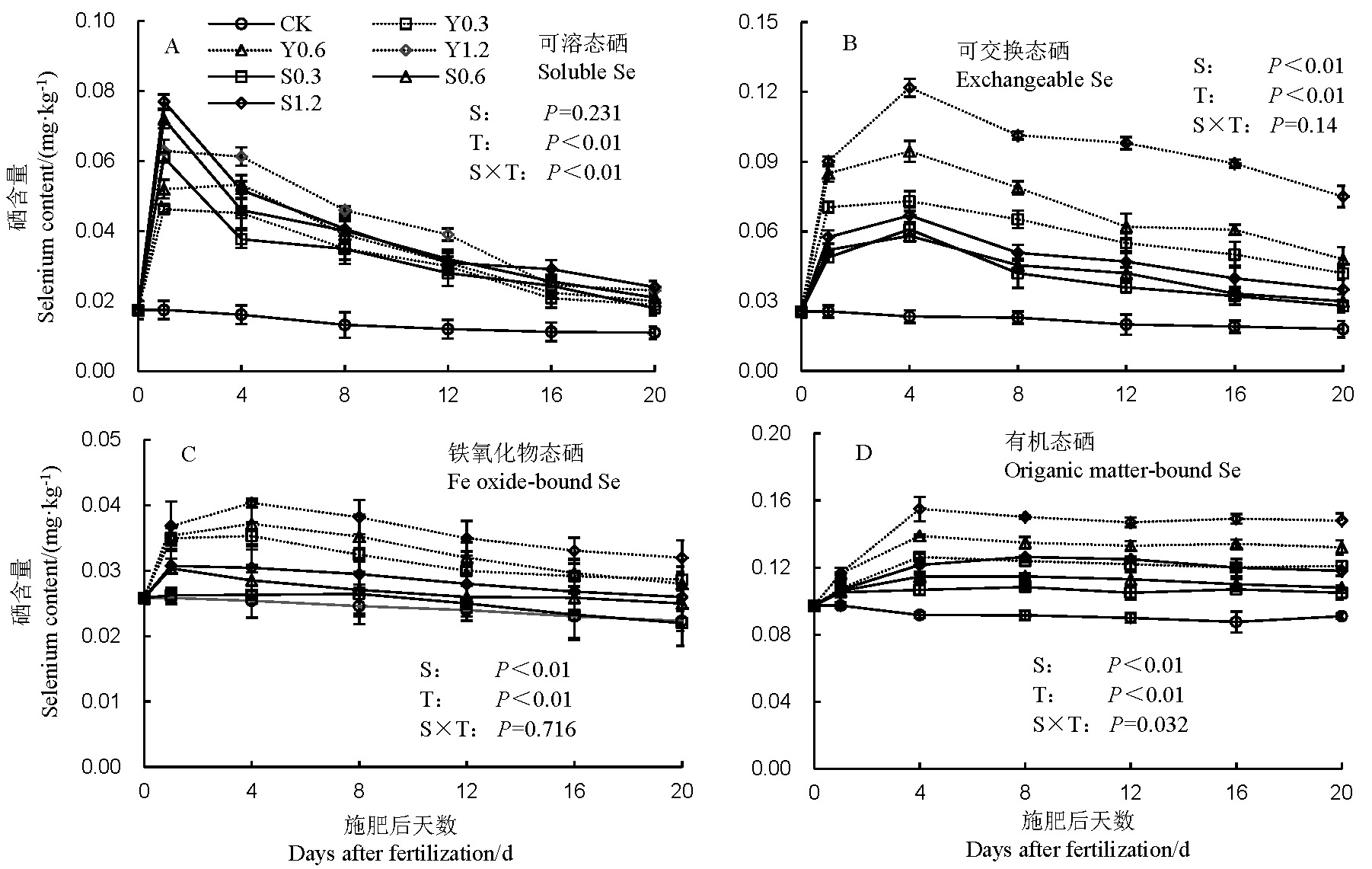
Fig. 1. Transformation of different valence selenium in soil. S indicate different valence selenium; T indicate different treatment time. S0.3, S0.6, S1.2 indicate selenate application levels of 0.3, 0.6 and 1.2 kg/hm2, respectively. Y0.3, Y0.6 and Y1.2, Selenite application levels of 0.3, 0.6 and 1.2 kg/hm2, respectively. The same as in figures and tables below.
| 处理 Treatment | 施硒量 Selenium application level / (kg·hm-2) | 硒含量 Selenium content /(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 籽粒 Grain | ||
| 对照 CK | 0 | 0.156±0.024 d | 0.063±0.003 c | 0.109±0.006 d | 0.024±0.003 f |
| 硒酸盐Selenate | 0.3 | 0.279±0.003 c | 0.083±0.004 c | 0.189±0.015 b | 0.078±0.005 c |
| 0.6 | 0.255±0.016 c | 0.116±0.006 b | 0.203±0.019 b | 0.106±0.002 b | |
| 1.2 | 0.345±0.026 b | 0.221±0.003 a | 0.301±0.003 a | 0.162±0.009 a | |
| 亚硒酸盐Selenite | 0.3 | 0.300±0.009 bc | 0.067±0.011 c | 0.097±0.006 d | 0.046±0.002 e |
| 0.6 | 0.419±0.007 a | 0.134±0.008 b | 0.142±0.010 c | 0.062±0.002 d | |
| 1.2 | 0.460±0.025 a | 0.205±0.019 a | 0.143±0.006 c | 0.076±0.001 c | |
| 两因素方差分析 (F值) Two-way ANOVA (F value) | |||||
| 不同价态硒(Se) Different valence of Se | 101.60* | 0.88n | 339.30* | 533.21* | |
| 施硒量(C) Selenium content | 195.81* | 324.16* | 130.20* | 515.84* | |
| Se×C | 27.12* | 4.77n | 61.25* | 103.87* | |
Table 1 Effects of Se valence on its contents in root, stem, leaf and grain of rice.
| 处理 Treatment | 施硒量 Selenium application level / (kg·hm-2) | 硒含量 Selenium content /(mg·kg-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 籽粒 Grain | ||
| 对照 CK | 0 | 0.156±0.024 d | 0.063±0.003 c | 0.109±0.006 d | 0.024±0.003 f |
| 硒酸盐Selenate | 0.3 | 0.279±0.003 c | 0.083±0.004 c | 0.189±0.015 b | 0.078±0.005 c |
| 0.6 | 0.255±0.016 c | 0.116±0.006 b | 0.203±0.019 b | 0.106±0.002 b | |
| 1.2 | 0.345±0.026 b | 0.221±0.003 a | 0.301±0.003 a | 0.162±0.009 a | |
| 亚硒酸盐Selenite | 0.3 | 0.300±0.009 bc | 0.067±0.011 c | 0.097±0.006 d | 0.046±0.002 e |
| 0.6 | 0.419±0.007 a | 0.134±0.008 b | 0.142±0.010 c | 0.062±0.002 d | |
| 1.2 | 0.460±0.025 a | 0.205±0.019 a | 0.143±0.006 c | 0.076±0.001 c | |
| 两因素方差分析 (F值) Two-way ANOVA (F value) | |||||
| 不同价态硒(Se) Different valence of Se | 101.60* | 0.88n | 339.30* | 533.21* | |
| 施硒量(C) Selenium content | 195.81* | 324.16* | 130.20* | 515.84* | |
| Se×C | 27.12* | 4.77n | 61.25* | 103.87* | |
| 处理 Treatment | 吸收系数 Absorption index | 初级转运系数 Primary transport index | 次级转运系数 Secondary transport index |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.581±0.009 d | 0.457±0.003 c | 0.350±0.007 c |
| S0.3 | 0.841±0.011 ab | 0.487±0.008 c | 0.575±0.006 b |
| S0.6 | 0.853±0.008 ab | 0.600±0.010 b | 0.693±0.004 a |
| S1.2 | 0.922±0.005 a | 0.759±0.008 a | 0.623±0.007 ab |
| Y0.3 | 0.717±0.003 c | 0.256±0.008 e | 0.317±0.006 c |
| Y0.6 | 0.800±0.009 bc | 0.329±0.009 d | 0.331±0.010 c |
| Y1.2 | 0.860±0.004 ab | 0.365±0.008 d | 0.373±0.009 c |
Table 2 Effects of Se valence on its absorption and transport coefficients of rice.
| 处理 Treatment | 吸收系数 Absorption index | 初级转运系数 Primary transport index | 次级转运系数 Secondary transport index |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.581±0.009 d | 0.457±0.003 c | 0.350±0.007 c |
| S0.3 | 0.841±0.011 ab | 0.487±0.008 c | 0.575±0.006 b |
| S0.6 | 0.853±0.008 ab | 0.600±0.010 b | 0.693±0.004 a |
| S1.2 | 0.922±0.005 a | 0.759±0.008 a | 0.623±0.007 ab |
| Y0.3 | 0.717±0.003 c | 0.256±0.008 e | 0.317±0.006 c |
| Y0.6 | 0.800±0.009 bc | 0.329±0.009 d | 0.331±0.010 c |
| Y1.2 | 0.860±0.004 ab | 0.365±0.008 d | 0.373±0.009 c |
| 处理 Treatment | 单株成穗数 Panicle number per plant | 每穗粒数 Grain numbers per panicle | 千粒重 Thousand grain weight /g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.3±0.6 a | 114.7±0.6 a | 22.6±0.3 a | 10 110±248.5 a |
| S0.3 | 11.3±0.6 a | 116.3±0.6 a | 22.4±0.6 a | 10 179±233.8 a |
| S0.6 | 12.0±1.0 a | 114.0±2.0 a | 21.7±1.2 a | 10 193±291.9 a |
| S1.2 | 11.3±0.6 a | 117.0±1.0 a | 22.4±0.2 a | 10 202±242.0 a |
| Y0.3 | 11.3±0.6 a | 116.0±1.0 a | 22.3±1.0 a | 10 084±241.2 a |
| Y0.6 | 11.3±0.6 a | 114.3±1.2 a | 22.9±0.2 a | 10 201±312.4 a |
| Y1.2 | 11.7±0.6 a | 116.3±1.5 a | 21.8±0.1 a | 10 200±338.0 a |
Table 3 Effects of Se valence on yield and its components.
| 处理 Treatment | 单株成穗数 Panicle number per plant | 每穗粒数 Grain numbers per panicle | 千粒重 Thousand grain weight /g | 产量 Yield/(kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.3±0.6 a | 114.7±0.6 a | 22.6±0.3 a | 10 110±248.5 a |
| S0.3 | 11.3±0.6 a | 116.3±0.6 a | 22.4±0.6 a | 10 179±233.8 a |
| S0.6 | 12.0±1.0 a | 114.0±2.0 a | 21.7±1.2 a | 10 193±291.9 a |
| S1.2 | 11.3±0.6 a | 117.0±1.0 a | 22.4±0.2 a | 10 202±242.0 a |
| Y0.3 | 11.3±0.6 a | 116.0±1.0 a | 22.3±1.0 a | 10 084±241.2 a |
| Y0.6 | 11.3±0.6 a | 114.3±1.2 a | 22.9±0.2 a | 10 201±312.4 a |
| Y1.2 | 11.7±0.6 a | 116.3±1.5 a | 21.8±0.1 a | 10 200±338.0 a |
| [1] | 李莉萍, 王军. 土壤-植物系统中硒的赋存形态及其分析方法研究进展. 热带农业科学, 2009, 29(2): 58-66. |
| Li L P, Wang J.Advances on existing form of analysis methods for selenium in soil-plant system.Chin J Trop Agric, 2009, 29(2): 58-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 赵中秋, 郑海雷, 张春光, 马建华. 土壤硒及其与植物硒营养的关系. 生态学杂志, 2003, 22(1): 22-25. |
| Zhao Z Q, Zheng H L, Zhang C G, Ma J H.Advance in the studies on selenium in soil and selenium biological effect.Chin J Ecol, 2003, 22(1): 22-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | Sharma S, Bansal A, Dhillon S K, Dhillon K S.Comparative effects of selenate and selenite on growth and biochemical composition of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plant Soil, 2010, 329(1-2) :339-348. |
| [4] | Cao Z H, Wang X C, Yao D H, Zhang X L, Wong M H.Selenium geochemistry of paddy soils in Yangtze River Delta.Environ Int, 2001, 26(6): 335-339. |
| [5] | Rayman M P.Food-chain selenium and human health: Emphasis on intake.Brit J Nutr, 2008, 100(2): 254-268. |
| [6] | Zhu Y G, Pilonsmits E A, Zhao F J, Williams P N, Meharg A A.Selenium in higher plants: Understanding mechanisms for biofortification and phytoremediation.Trends Plant Sci, 2009, 14(8): 436-442. |
| [7] | Miguel N A, Carmen C V.Selenium in food and the human body: A review.Sci Total Environ, 2008, 400(1-3): 115-141. |
| [8] | Haug A, Graham R D, Christophersen O A, Lyons G H.How to use the world's scarce selenium resources efficiently to increase the selenium concentration in food.Microb Ecol Health Dis, 2007, 19(4): 209-228. |
| [9] | Keskinen R, Turakainen M, Hartikainen H.Plant availability of soil selenate additions and selenium distribution within wheat and ryegrass.Plant Soil, 2010, 333(1): 301-313. |
| [10] | Harada T, Takahashi Y.Origin of the difference in the distribution behavior of tellurium and selenium in a soil-water system.Geochem Cosmo Chim Acta, 2008, 72(5): 1281-1294. |
| [11] | Banuelos G S, Lin Z Q.Phytoremediation management of selenium-laden drainageediments in the San Luis Drain: A greenhouse feasibility study.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2005, 62(3): 309-316. |
| [12] | 瞿建国,徐伯兴,龚书椿. 氢化物发生-无色散原子荧光光度法测定土壤中有效态硒和总硒. 土壤通报, 1998, 29(1): 47-53. |
| Qu J G, Xu B X, Gong S C.Determination of bio-available and total selenium in soil by hydride generation non-dispersive AFS.Chin J Soil Sci, 1998, 29(1): 47-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] | Gangadhara, Kumar P R, Prakash V. The structure functional catalytic activity of rice brain lipase in the presence of selenium and lithium.Europ Food ResTechnol, 2010, 230(4): 551-557 |
| [14] | 周鑫斌, 施卫明, 杨林章. 水稻子粒硒累积机制研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(3): 503-507. |
| Zhou X B, Shi W M, Yang L Z.Study on mechanisms of seleniumaccumulation in rice grains.Plant Nutr Fert Sci, 2008, 14(3): 503-507. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 王松山, 吴雄平, 梁东丽, 薛瑞玲,鲍俊丹. 不同价态外源硒在石灰性土壤中的形态转化及其生物有效性. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(12): 2499-2505. |
| Wang S S, Wu X P, Liang D L, Xue R L, Bao J D.Transformation and bioavailability for Pak choi (Brassica chinensis) of different forms of selenium added to calcareous soil. Acta Sci Circum, 2010, 30(12): 2499-2505. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 于振, 李建科, 李梦颖,马倩倩, 黄瑞蕊, 何晓叶,李佳. 食品中微量硒测定方法研究进展. 食品工业科技, 2012, 33(18): 371-377. |
| Yu Z, Li J K, Li M Y, Ma Q Q, Huang R R, He X Y, Li J.Research progress in determination of trace selenium in food.Sci Technol Food Ind, 2012, 33(18): 371-377. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 姜超强, 沈嘉, 祖朝龙. 水稻对天然富硒土壤硒的吸收及转运. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(3): 809-816. |
| Jiang C Q, Sheng J, Zu C L.Selenium uptake and transport of rice under different Se-enriched natural soils.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2015, 26(3): 809-816. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 王松山. 土壤中硒形态和价态及生物有效性研究. 杨陵:西北农林科技大学,2012. |
| Wang S S.Fractionation and speciation of selenium in soil and its bioavailability.Yangling: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | Fujita M, Ike M, Hashimoto R, Nakagawa T, Yamaguchi K, Soda S O.Characterizing kinetic of transport and transformation of selenium in water-sediment microcosm free from selenium contamination using a simple mathematical model.Chemosphere, 2005, 58(6): 705-714. |
| [20] | Munier-Lamy C, Deneux-Mustin S, Mustin C,Merlet D, Berthelin J, Leyval C.Selenium bioavailability and uptake as affected by four different plants in a loamy clay soil with particular attention to mycorrhizae inoculated ryegrass. JEnvir Radioac, 2007, 97(2-3): 148-158. |
| [21] | 黄青青. 水稻和小麦对硒的吸收、转运及形态转化机制.北京:中国农业大学, 2015. |
| Huang Q Q.Mechanisms of selenium uptake, translocation and speciation transformation in rice and wheat. Beijing: China Agric ultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | Sun G X,Liu X, Williams P N, Zhu Y G.Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to grain and its speciation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa L). Environ Sci Technol, 2010, 44(17) : 6706-6711. |
| [23] | 董广辉, 陈利军, 武志杰. 植物硒素营养及其机理研究进展. 应用生态学报, 2002,13(11): 1487-1490. |
| Dong G H, Chen L J, Wu Z J.Research advances in plant selenium nutrition and its mechanism.Chin J Appl Ecol, 2002, 13(11): 1487-1490. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [24] | Li J, Liang D, Qin S, Feng P, Wu X.Effects of selenite andselenate application on growth and shoot selenium accumulation of pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) during successive planting conditions. Environ Sci Poll Res, 2015, 22(14):11076-86. |
| [1] | GUO Zhan, ZHANG Yunbo. Research Progress in Physiological,Biochemical Responses of Rice to Drought Stress and Its Molecular Regulation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 335-349. |
| [2] | WEI Huanhe, MA Weiyi, ZUO Boyuan, WANG Lulu, ZHU Wang, GENG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xiang, MENG Tianyao, CHEN Yinglong, GAO Pinglei, XU Ke, HUO Zhongyang, DAI Qigen. Research Progress in the Effect of Salinity, Drought, and Their Combined Stresses on Rice Yield and Quality Formation [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 350-363. |
| [3] | XU Danjie, LIN Qiaoxia, LI Zhengkang, ZHUANG Xiaoqian, LING Yu, LAI Meiling, CHEN Xiaoting, LU Guodong. OsOPR10 Positively Regulates Rice Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 364-374. |
| [4] | CHEN Mingliang, ZENG Xihua, SHEN Yumin, LUO Shiyou, HU Lanxiang, XIONG Wentao, XIONG Huanjin, WU Xiaoyan, XIAO Yeqing. Typing of Inter-subspecific Fertility Loci and Fertility Locus Pattern of indica-japonica Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 386-396. |
| [5] | DING Zhengquan, PAN Yueyun, SHI Yang, HUANG Haixiang. Comprehensive Evaluation and Comparative Analysis of Jiahe Series Long-Grain japonica Rice with High Eating Quality Based on Gene Chip Technology [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 397-408. |
| [6] | HOU Xiaoqin, WANG Ying, YU Bei, FU Weimeng, FENG Baohua, SHEN Yichao, XIE Hangjun, WANG Huanran, XU Yongqiang, WU Zhihai, WANG Jianjun, TAO Longxing, FU Guanfu. Mechanisms Behind the Role of Potassium Fulvic Acid in Enhancing Salt Tolerance in Rice Seedlings [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 409-421. |
| [7] | LÜ Zhou, YI Binghuai, CHEN Pingping, ZHOU Wenxin, TANG Wenbang, YI Zhenxie. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rate and Transplanting Density on Yield Formation of Small Seed Hybrid Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 422-436. |
| [8] | HU Jijie, HU Zhihua, ZHANG Junhua, CAO Xiaochuang, JIN Qianyu, ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHU Lianfeng. Effects of Rhizosphere Saturated Dissolved Oxygen on Photosynthetic and Growth Characteristics of Rice at Tillering Stage [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 437-446. |
| [9] | WU Yue, LIANG Chengwei, ZHAO Chenfei, SUN Jian, MA Dianrong. Occurrence of Weedy Rice Disaster and Ecotype Evolution in Direct-Seeded Rice Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 447-455. |
| [10] | LIU Fuxiang, ZHEN Haoyang, PENG Huan, ZHENG Liuchun, PENG Deliang, WEN Yanhua. Investigation and Species Identification of Cyst Nematode Disease on Rice in Guangdong Province [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(4): 456-461. |
| [11] | CHEN Haotian, QIN Yuan, ZHONG Xiaohan, LIN Chenyu, QIN Jinghang, YANG Jianchang, ZHANG Weiyang. Research Progress on the Relationship Between Rice Root, Soil Properties and Methane Emissions in Paddy Fields [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 233-245. |
| [12] | MIAO Jun, RAN Jinhui, XU Mengbin, BO Liubing, WANG Ping, LIANG Guohua, ZHOU Yong. Overexpression of RGG2, a Heterotrimeric G Protein γ Subunit-Encoding Gene, Improves Drought Tolerance in Rice [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 246-255. |
| [13] | YIN Xiaoxiao, ZHANG Zhihan, YAN Xiulian, LIAO Rong, YANG Sijia, Beenish HASSAN, GUO Daiming, FAN Jing, ZHAO Zhixue, WANG Wenming. Signal Peptide Validation and Expression Analysis of Multiple Effectors from Ustilaginoidea virens [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 256-265. |
| [14] | ZHU Yujing, GUI Jinxin, GONG Chengyun, LUO Xinyang, SHI Jubin, ZHANG Haiqing, HE Jiwai. QTL Mapping for Tiller Angle in Rice by Genome-wide Association Analysis [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 266-276. |
| [15] | WEI Qianqian, WANG Yulei, KONG Haimin, XU Qingshan, YAN Yulian, PAN Lin, CHI Chunxin, KONG Yali, TIAN Wenhao, ZHU Lianfeng, CAO Xiaochuang, ZHANG Junhua, ZHU Chunqun. Mechanism of Hydrogen Sulfide, a Signaling Molecule Involved in Reducing the Inhibitory Effect of Aluminum Toxicity on Rice Growth Together with Sulfur Fertilizer [J]. Chinese Journal OF Rice Science, 2024, 38(3): 290-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||